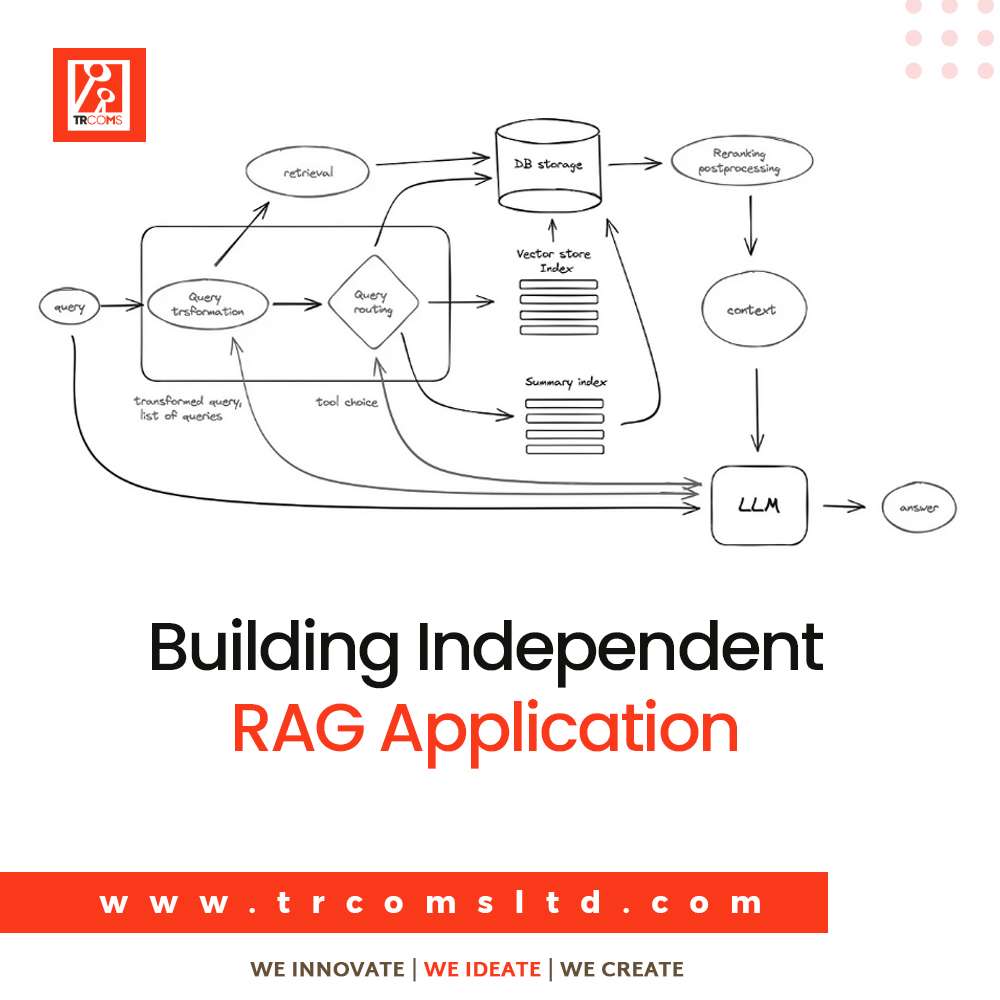
Building RAG application Without Azure AI Search.
Having worked on several AI projects from scratch, I strive not to depend on any single service, ensuring that projects can be easily transferred to other services. I have observed many startup founders who overlook long-term technology goals, focusing solely on building without proper planning. This guide aims to help you build a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) application without relying on Azure AI Search, leveraging open-source tools and other cloud services.
Key Components of a RAG Application:
- Document Storage: Store your documents or knowledge base.
- Vector Database: This is used to store embeddings and perform similarity searches.
- Embedding Model: To convert text into vector representations.
- Retrieval System: To retrieve relevant documents based on user queries.
- Generation Model: To generate responses using the retrieved documents.

Steps to Build a RAG Application:
Set Up Document Storage:
Use a traditional database (PostgreSQL, MongoDB) or cloud storage (AWS S3, Google Cloud Storage) to store your documents.
Ensure documents are indexed for efficient retrieval.
Embedding Model:
Use pre-trained models like OpenAI’s GPT, Hugging Face’s Transformers (e.g., BERT, RoBERTa), or Sentence Transformers.
Convert documents and user queries into embeddings.
Vector Database:
Use open-source vector databases like Pinecone, Weaviate, Milvus, or FAISS for storing and querying embeddings.
These databases support fast similarity searches, which is critical for retrieving relevant documents.
Retrieval System:
Implement a retrieval mechanism that queries the vector database based on user embeddings.
Retrieve the top N most similar documents.
Response Generation:
Use a generation model (e.g., GPT-based models) to generate responses.
Combine the retrieved documents with the user query as input to the model for context-aware generation.
Orchestration:
Build a backend service (using Python, Node.js, etc.) to handle the flow:
Accept user queries.
Generate embeddings for the query.
Retrieve relevant documents.
Generate responses.
Deploy the service on a cloud platform (AWS, Google Cloud, DigitalOcean) or on-premises.
Tools and Technologies:
Embedding Models: Hugging Face Transformers, OpenAI GPT
Vector Databases: Pinecone, Weaviate, Milvus, FAISS
Document Storage: PostgreSQL, MongoDB, AWS S3
Backend Development: Flask, FastAPI (Python), Express (Node.js)
Deployment: Docker, Kubernetes, Cloud platforms (AWS, GCP)
Example Workflow:
User Query: “How does photosynthesis work?”
Generate Embedding: Convert the query into a vector.
Retrieve Documents: Search the vector database for relevant documents on photosynthesis.
Generate Response: Use the retrieved documents to generate a comprehensive answer.
Considerations:
Performance: Optimize the vector database and embedding model for low-latency retrieval.
Scalability: Ensure the system can handle increased load by scaling horizontally.
Accuracy: Fine-tune the embedding and generation models to improve the relevance and quality of responses.
By using these components and steps, you can build a robust RAG application without relying on Azure AI Search, leveraging open-source tools and cloud services.